
Digital security threats like ransomware and phishing attacks frequently make headlines these days. One would hope this publicity translates into heightened awareness and more secure behavior online by web users. To test this theory, Wombat Security surveyed more than 2,000 working adults (1,000 in the United States and 1,000 in the United Kingdom) in early May 2017 about digital security topics and what they're doing to defend themselves. The results reveal that users have a long way to go towards advancing their awareness of some of today's most fundamental digital security risks. Provided below are the main findings of Wombat Security's first-ever User Risk Report.
Lacking Awareness of Phishing and Ransomware
Respondents in the UK and the US demonstrated equal levels of awareness for phishing. Seventy percent of participants gave a correct definition for the digital security threat but 30 percent revealed they still don't know about phishing. Thirteen percent didn't even harbor a guess as to what phishing entails. Such ignorance exists in spite of the fact that 43 percent of US respondents and 19 percent of UK surveyed individuals said they've fallen for a phishing attack at some point in their lives. Users' awareness of ransomware was only worse. Less than half of US and UK respondents correctly defined crypto-malware at 37 percent and 42 percent, respectively. This means nearly 60 percent of all participants didn't know anything about ransomware. To be fair, ransomware awareness has probably since improved; Wombat Security conducted its survey just prior to the global WannaCry outbreak on May 12.
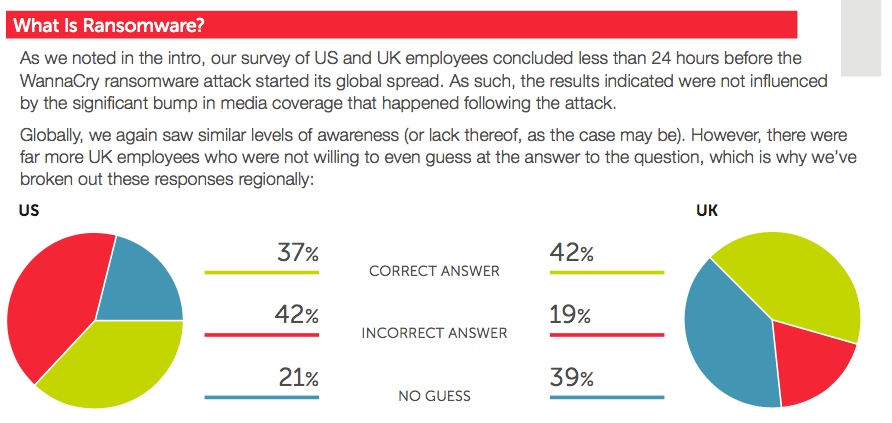
2017 User Risk Report page 4 Fortunately, more than four in five respondents in both countries said they regularly back up their data. Hopefully they'll remember those backups if they suffer a ransomware infection.
Misconceptions of Threats Abound
Insufficient awareness of digital security threats jeopardizes users' data. But so too do popular misconceptions. For instance, more than half (57 percent) of US respondents to Wombat Security's survey said they can trust the free Wi-Fi service of a trusted location like a coffee shop or hotel to keep their information safe. Just over a quarter (27 percent) of UK individuals surveyed felt the same. In reality, free and public Wi-Fi service offers attackers ample opportunity to intercept users' data. Acknowledging these threats, users should refrain from doing any banking on a public Wi-Fi network. They should also consider using a VPN. Overall, most survey respondents also placed too much faith in their anti-virus software. Fifty-eight percent of US respondents and 37 percent of UK respondents said their solution can protect them against a digital attack. That perception might have held true in the 90s. But in an era of file-less malware, it's no longer the case. Perhaps the most troubling misconception was some respondents' inability to correctly define malware. Only 78 percent of UK individuals and 61 percent of US participants said malware is "software that harms devices and files." Most of the remaining users said it's "hardware that boosts Wi-Fi signals" or a "mobile app that delivers real-time alerts." Others said they had no idea what malware is. As a sizable portion of online users can't define malware or actually think it's something that can help them, it's clear that companies can do a lot more to train their employees about digital security threats.
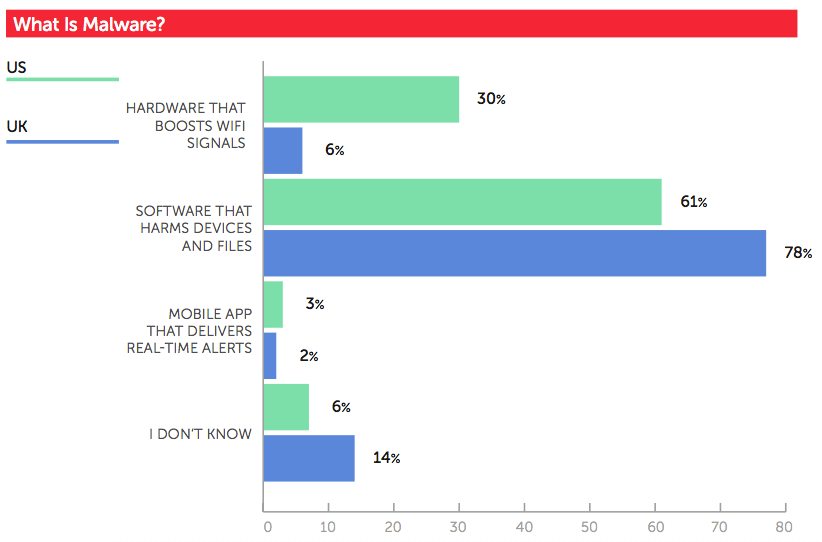
2017 User Risk Report page 2
Passwords, Mobile (In)security, and Corporate Device (Ab)use
Most users take the security of their web accounts, mobile phones, and corporate devices seriously, but there is room for improvement. To illustrate, approximately half of US respondents and UK participants reported they use a password manager or have a different password for every web account at 67 percent and 45 percent, respectively. The remainder revealed that they use fewer than 10 passwords to protect their entire digital presence, with some utilizing as few as one or two passwords. On their mobile devices, more than half (54 percent) of respondents stated they protect their phones with biometric authentication, a complex swipe pattern, or an alphanumeric password. Thirty-five percent disclosed their choice of a 4- or 6-digit PIN, a locking mechanism which provides a small degree of mobile security. Even so, 11 percent of users said they don't protect their devices at all. Attackers can easily exploit this oversight and access sensitive information if they gain physical access to an unprotected device.
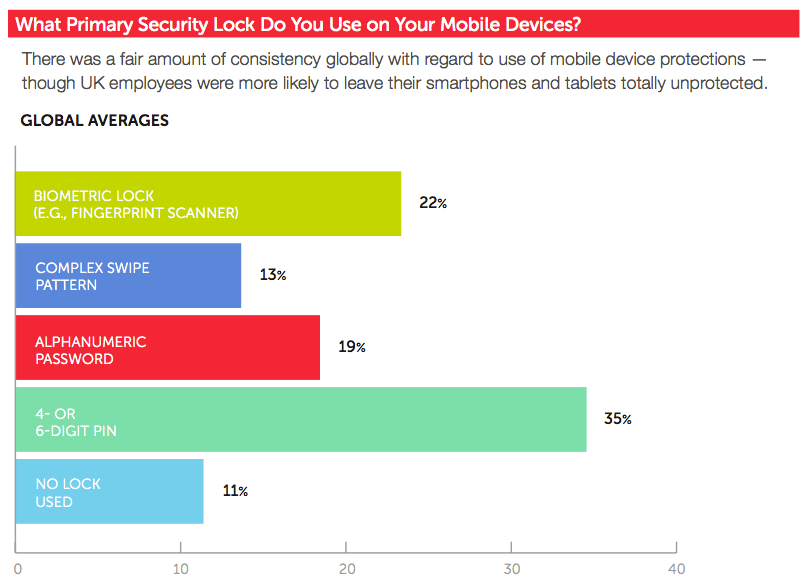
2017 User Risk Report page 8 As for corporate laptops, 71 percent of US respondents and 26 percent of UK respondents claimed to use a VPN on their company-issued devices. Perhaps this security measure helps 71 percent of US individuals surveyed 39 percent of UK participants feel justified in regularly using their corporate device at home. Most respondents said they use their device for checking and responding to email, but there are plenty of others that admitted to checking social media, streaming media, and shopping online.
Recommendations for Building Awareness
If one thing's clear from the User Risk Report 2017, it's that companies still have work to do with improving their employees' security awareness. Wombat Security couldn't agree more:
"Sure...it’s probable that, in the wake of the WannaCry attack, employees’ recognition of what ransomware is has increased. But it took a major global event to create that probability. Regardless, greater awareness of ransomware — or any cybersecurity threat — is not the same as knowing how to avoid that threat."
To address that provide, the security awareness training provider recommends that organizations focus on ongoing security training and awareness campaigns. This two-front effort can help create a workforce that not only make informed decisions about their digital security. It can also help employees play an active part in spotting threats and responding to issues before they snowball into major security incidents. For more findings on user awareness of digital security topics, download Wombat Security's report here.

