Qatar is one of the wealthiest countries in the world. Finances Online, Global Finance Magazine and others consider it to be the wealthiest nation. This is because the country has a small population of under 3 million but relies on oil for the majority of its exports and Gross Domestic Product (GDP). These two factors helped to push the country’s GDP measured at purchasing power parity (PPP) to over 132,886, per Global Finance Magazine’s findings in August 2020. Such wealth constitutes abundant opportunities for growth, including in the mind of Qatar’s General Secretariat for Development Planning all the way back in 2008. That’s why the agency decided to publish the National Vision 2030. This strategy sets out the aim to make Qatar into an advanced society by pursuing social, human, economic and environmental development.
Introducing the National Information Assurance Policy
To achieve the National Vision 2030 in full, Qatar’s Ministry of Transport and Communication (MOTC) recognized the need to secure the information flowing through the country’s information and communications technology (ICT). MOTC responded by creating the National Information Assurance (NIA) Policy. The document both defines a governance policy as well as elucidates policies and procedures that Qatari government agencies can use to safeguard ICT data flows, thereby providing those entities with a baseline for ensuring secure communications. So, how can organizations ensure compliance with the NIA Policy? To answer that question, this blog post will first examine how organizations can accurately classify their IT processes under the NIA Policy. It will then explain some of the security controls recommended by the MOTC that organizations can use to safeguard their processes. Finally, it will discuss how to use Tripwire Enterprise to remain compliant with the NIA Policy.
Data Classification under the NIA Policy
MOTC specifies that in-scope agencies can classify their data by first conducting a Business Impact Analysis (BIA) of their IT processes. This step should involve determining how the loss or degradation of a process could affect the organization’s reputation, external environment (including other agencies), internal environment (including its employees), legal obligations and revenue. For each of those impact factors, the agency must rate the factor’s importance on a scale of 0 (Not Important) to 4 (Not high importance). They must also determine the impact that a loss or degradation of a process would have on the organization on a similar scale of 0 (No impact) to 4 (Very high impact). They will then use the formula impactvalue = 1.25 (α1I1 + α2I2 + α3I3 + α4I4 + α5I5) to calculate the criticality of each process. Simultaneously, organizations need to account for their dependent assets by classifying their information assets along with their corresponding levels of security protection. They must do this by first identifying the processes, their owners and their dependencies including data, apps, networks and systems. At that point, organizations should determine the security classification for each asset using a system of Low (L), Medium (M) and High (H). They then need to record the aggregate security level for each of their information assets along with the full security classification that reflect the ideal level of every asset’s availability, integrity and confidentiality.
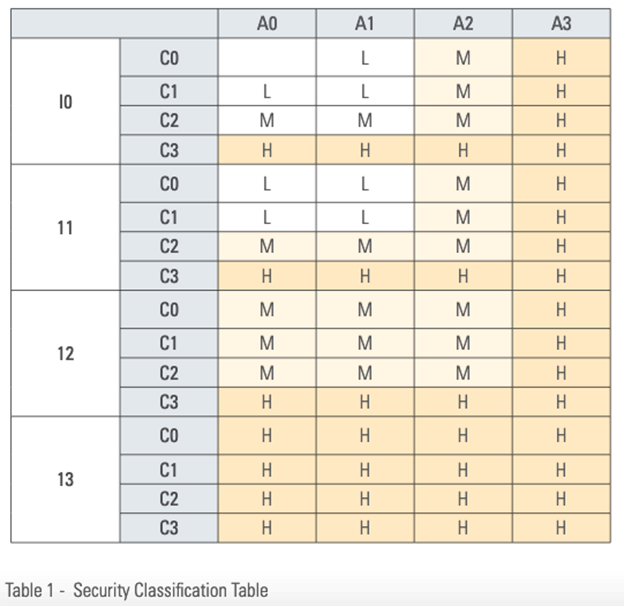
Having completed the steps identified above, organizations should prioritize their assets based upon their criticality first and foremost to the State of Qatar as a whole and then to their own functionality. They must use those calculations to develop a compliance plan that reflects the compliance priority of their processes and their dependent information assets. The plan should also contain information for scheduling assessments and implementing controls.
Implementing the Appropriate Controls
As noted in the NIA Policy, information security is more than a technical issue. It also consists of security governance, or policies and controls through which the organization can direct its security efforts. MOTC explains that there’s only one way to make security governance work: For security to be effective, it must be included in all organizational and business processes from end to end - physical, operational and technical. A formal information security strategy must be implemented by developing comprehensive information security policies consistent with the goals and mission of the organization. To provide effective governance, a set of enterprise standards for each policy must be developed to provide defined boundaries for acceptable processes and procedures. Education, training and awareness must also be considered to convey information to all personnel as part of an ongoing process to change behaviours not conducive to secure, reliable operations. In support of this overarching philosophy, organizations must follow an implementation manual provided in the NIA policy. This document highlights the following security standards:
- Build a proper governance structure that’s headed by a responsible Security Manager.
- Define a risk management procedure.
- Ensure that outsourced services remain compliant with the NIA Policy.
- Label all information assets correctly in order to maximize data protection efforts.
- Document, review and manage changes that deviate from assets’ configuration baselines.
- Ensure security processes cohere with processes upheld by HR.
- Invest in creating an ongoing security awareness program for the entire workforce.
- Appoint someone to serve as the head of the incident management program.
- Update the business continuity plan on an ongoing basis.
- Monitor for and log all instances of unauthorized data, app or system access.
- Settle on a data retention period that suits the information stored by the agency.
- Document all of these processes together in a written security policy.
- Submit to an audit of the entire infrastructure at least once a year.
It also includes general prescriptions for how organizations can secure their systems, media and other parts of their network. These guidelines include changing passwords every 90 days, documenting procedures for the sanitization of media devices and employing strong wireless security protocols such as WPA2 and EAP-TLS.
How Tripwire Can Help Organizations Comply with the NIA Policy
Tripwire Enterprise can help in-scope entities to comply with the NIA Policy. That’s because Tripwire’s solution has out-of-the-box policies for NIA compliance auditing among other best practice frameworks. As an example, here are four security aspects of the NIA Policy with which Tripwire Enterprise can support Qatari agencies:
- Network Security: Create a baseline governing the use of and connections to IT networks within the organization’s infrastructure.
- Access Control Security: Protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of an information asset using measures that control who can access it.
- Software Security: Integrate security into the software development and acquisition phases from the start rather than bolting it on.
- Cryptographic Security: Establish a baseline for the implementation of encryption in order to uphold the integrity of confidential assets.
Speaking of integrity, Tripwire Enterprise can help organizations to uphold the integrity of their systems, audit trails and IT assets. It does this via its secure configuration management (SCM) capabilities. Such functionality enables organizations to monitor their assets’ configurations for deviations from their approved baselines and to recover from configuration drift. For more information on how Tripwire can help your organization maintain compliance with the NIA Policy, click here.
Mastering Security Configuration Management
Master Security Configuration Management with Tripwire's guide on best practices. This resource explores SCM's role in modern cybersecurity, reducing the attack surface, and achieving compliance with regulations. Gain practical insights for using SCM effectively in various environments.

