
A newly discovered PayPal phishing scam attempts to steal much more than just a user's login credentials for the online payments service. Slovakian security firm ESET observed that the scam began by targeting users with an attack email warning them of unusual activity involving their account. The email urged recipients to click on an embedded link so as to secure their account and protect their financial information. In instances of compliance, the scam redirected users to one of several websites that used PayPal-themed branding to reiterate the farce of unusual account activity. To its credit, these websites used clever names and valid SSL certificates to add a sense of legitimacy. Yet they nevertheless gave themselves away as fake by their use of non-PayPal domains, substandard English and CAPTCHAs.
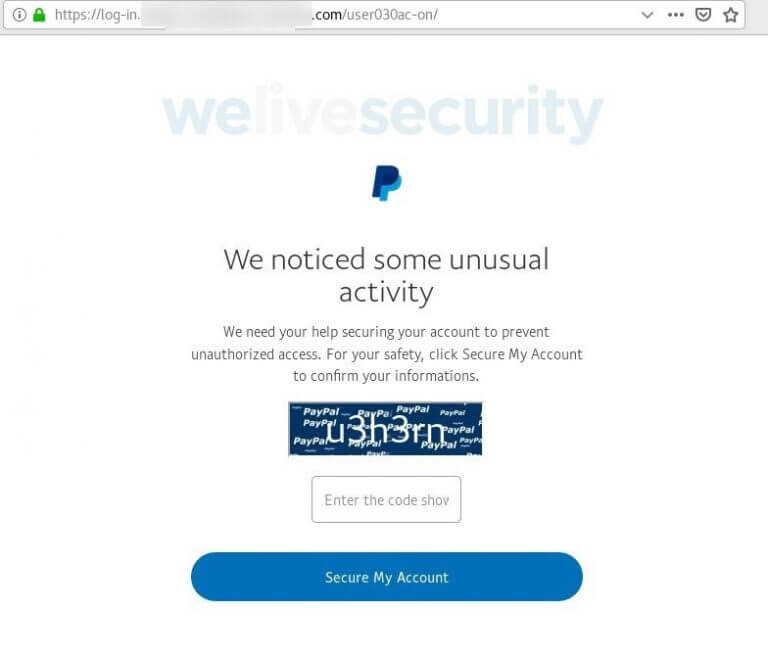
The page that the campaign presents to the user after they fall for the bait. (Source: ESET) Clicking on the "Secure My Account" button prompted users to submit their PayPal credentials. But as ESET explains in its research, the scam didn't end there by a long shot:
By this stage, you have already handed over your PayPal login credentials; nevertheless, the scammers attempt to collect far more than that. As Figures 6 to 9 show, in a series of steps you’re asked to surrender a range of sensitive information, including your credit or debit card data, access credentials to the bank account linked to the card and, lastly, the login to your email account.
At that point, the scam reassured the user that their account was secure. In reality, the user had forfeited several pieces of their personal and financial information, data which an attacker could then use to commit identity theft and credit card fraud. Users can protect themselves against the scam described above by familiarizing themselves with some of the most common types of phishing campaigns in circulation today. They should also exercise caution around suspicious links and email attachments, not to mention implement two-factor authentication (2FA) on their email, banking and PayPal accounts.
Meet Fortra™ Your Cybersecurity Ally™
Fortra is creating a simpler, stronger, and more straightforward future for cybersecurity by offering a portfolio of integrated and scalable solutions. Learn more about how Fortra’s portfolio of solutions can benefit your business.

