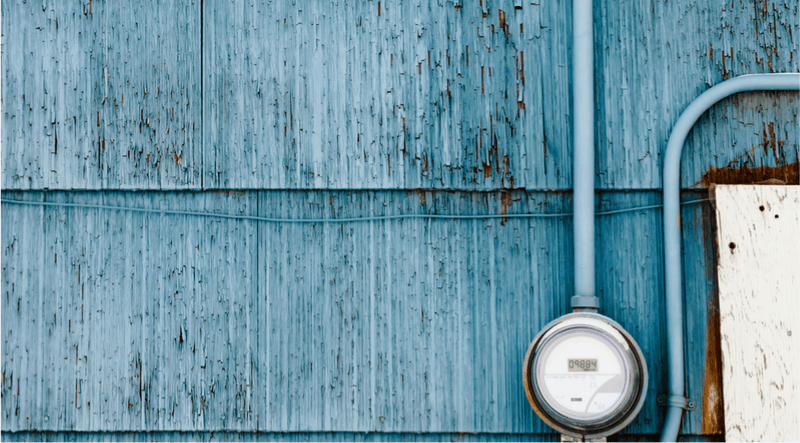

Utilities can be a pricey monthly expense for many households and businesses, with the average cost for households in America coming in at over $420 every month. Getting on top of utility usage, especially electricity—which typically constitutes the largest part of that monthly expense—can help save money, but it can also help conserve resources and avoid wastefulness. The first step to shaving down utility usage is figuring out how much you’re using and where it’s all going. One method of doing this is smart metering, which uses a connected device to collect and share data and allow users to see how their usage shakes out each month. Smart meters are becoming a common part of many homes and businesses. In the UK, government regulation dictates that energy suppliers must offer smart meters to homes and small businesses. However, install is behind schedule, with large energy suppliers installing just 9.7 meters a minute. Although that may sound significant, that rate will need to triple if these suppliers are to meet the 2020 deadline laid out by the Smart Energy Code. Ideally, if these suppliers are able to pick up the pace and complete install on-time, millions of households and businesses in the UK will soon have smart meters operating round-the-clock, setting the stage for other countries, like the US, to follow suit. However, with all their benefits, smart meters carry some risk, and it’s important to be aware of both the benefits of and threats to smart meters as they become a standard part of all our lives.
What is smart metering?
Smart meters track usage of specific utilities to help users recognize their usage patterns and adjust behaviors accordingly as well as provide accurate usage readings to energy providers. Popular smart meters range in price from less than $100 to upwards of $300. In the United States, most smart meters are installed in residential homes. But businesses, too, can glean value from their functions. Regardless of the user, smart meters use a communication network called the Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) to connect and transmit data.
Uses and benefits of smart meters
Smart meters are convenient both for users and their suppliers. By capturing and sharing an accurate reading of energy usage, smart meters allow energy providers to bill users with precision based on their actual usage amounts as opposed to estimates or in-person meter reads, which are both standard methods of billing. In addition, smart meters provide users with in-depth information about their own energy usage, which can help them be more conscientious about their energy consumption and narrow in on the areas where they are using energy most heavily. Both parties, whether in home or business situations, will benefit from more accurate data conveyed in a more convenient way and should see lowered bills and smaller energy consumption after making behavioral changes informed by that data. There’s another less-obvious benefit that up-to-date data collection provides for energy providers. This data can help show usage patterns in specific areas, meaning companies have a more clear vision of demand. Providers can see the potential for blackouts in heavy use times in certain areas and enact counter-measures to prevent overloading, including charging users based on time and area demand.
Security risks of smart meters
With all the benefits they provide, smart meters may seem like an easy solution to any energy setup. However, as with any connected device, smart meters pose some security risk to users. One clear problem is the constantly transmitting nature of the device. Once connected to the AMI (which provides an access point for hackers and other malicious actors), smart meters transmit data 24/7, leaving an all-day window for attack. From there, hackers can adjust bills, take payment information and more, often without either party ever knowing. Although there haven’t been any major attacks through smart meters yet, it’s important for energy providers, and the users they supply, to stay on top of device security. An attack is the wrong time to be thinking about security; instead, stakeholders should make sure to maintain secure connections and use connected devices wisely all the time to ensure ongoing security.
Moving forward
As smart metering becomes an important part of energy usage in the UK, the USA and beyond, it will become increasingly important for energy companies to figure out ways to keep them secure. Tripwire features products to help identify and defend against threats, as well as make necessary reports in case an attack happens. By integrating security solutions into your metering system, you’ll find more safety in an era of ever-present cyber threat. In spite of all the risk factors, smart meters are still considered a safe device and are relatively well-protected from attacks, but users and providers alike will need to stay on their toes to make sure they remain the only ones collecting information. To learn more about the march towards achieving and maintaining compliance, the Smart Energy Code (SEC) defines the rights and obligations of energy suppliers, network operators and other relevant parties involved in the end-to-end management of smart metering in Great Britain. See how Tripwire can help you here.
About the Author: Alex Haslam is a tech writer specializing in technology’s human connection — how it affects our lives, careers, and relationships, and how we can use it to keep ourselves and our data safe. She contributes regularly to several top-tier tech publications and is working to help increase tech literacy through writing about today’s technology in an accessible way. Editor’s Note: The opinions expressed in this guest author article are solely those of the contributor, and do not necessarily reflect those of Tripwire, Inc.
Meet Fortra™ Your Cybersecurity Ally™
Fortra is creating a simpler, stronger, and more straightforward future for cybersecurity by offering a portfolio of integrated and scalable solutions. Learn more about how Fortra’s portfolio of solutions can benefit your business.

